Cancer – Common Risk Factors and Preventative Measures
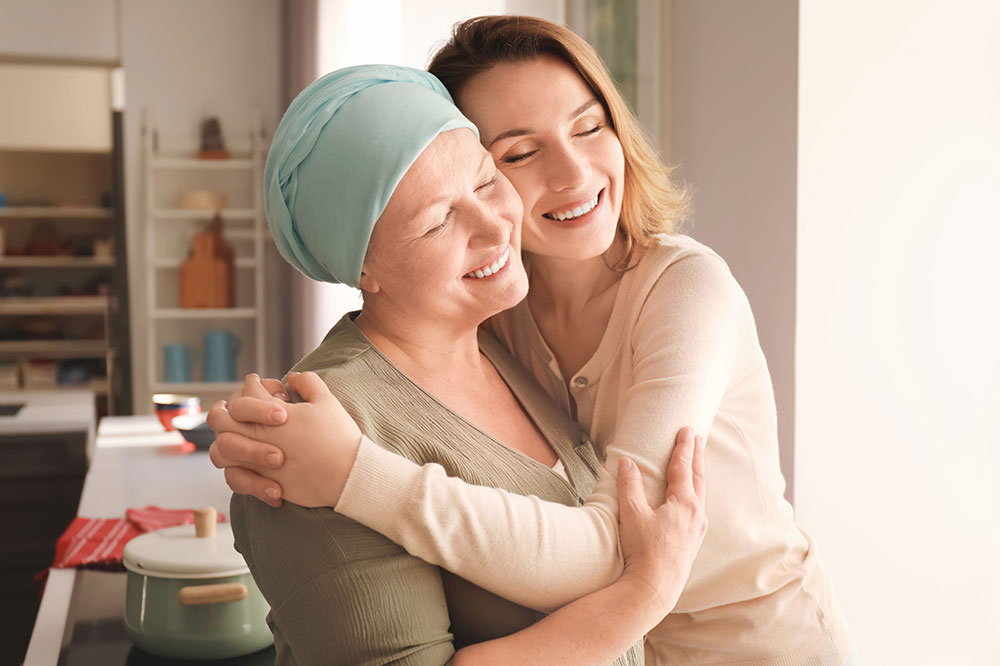
Cancer is not a singular disease but a term used to describe several conditions that may cause cells to multiply rapidly anywhere in the human body. These cells invade healthy tissues in the body and can cause a mutation that cannot be cured. Cancer can also spread throughout the body through the lymphatic (lymph nodes) system or the circulatory system if left unchecked. It helps to know and understand the risks for early diagnosis, possible prevention, and timely treatment.
Risk factors for most common types of cancer:
1. Age
The body’s immunity and ability to regenerate healthy cells deteriorates with advancing age. The median age for cancer is determined to be 66 years, which means half of the cases are detected among those below 33 years. This includes men, women, and children.
2. Genetic factors
Genetics is one of the major risk factors observed among common types of cancer. A family history of people who have suffered from some form of cancer increases the risk for the future generation. Specific genetic syndromes and autoimmune disorders can also trigger cancer among those who are already experiencing symptoms.
3. Lifestyle choices
Smoking, chewing tobacco, or consuming alcohol above the recommended limit also increases the risk among young and older people. Tobacco and cigarettes contain harmful carcinogens that further trigger digestive and respiratory problems. Even secondhand inhalation of such carcinogens can be harmful.
4. Obesity
Obesity can trigger about 40% of all known cancers. The risk is high among Americans, as a majority of the population is overweight. That does not necessarily exclude people belonging to diverse ethnicities. Being obese in general can lead to 13 different types of cancer.
5. Improper diet and inactivity
Lack of nutrition and leading a sedentary lifestyle also puts men and women at equal risk of developing certain types of tumors and cancers. The immune system requires a balanced diet rich in essential vitamins, nutrients, and minerals. Any deficit can trigger an autoimmune response that leads to cancer.
6. Infections and UV exposure
Certain types of bacteria and viruses can trigger infectious diseases that may trigger cancer cells to mutate and multiply rapidly. Prolonged exposure to UV rays and radiation used for treating some diseases also increases the risk of cancer.
Preventing cancer
There are more than a hundred different types of cancer known to medical professionals. Early diagnosis of cancer can allow healthcare professionals to formulate an effective plan to manage the symptom. Cancer cannot be cured, and at best, medications, surgery, treatment, and therapy can help improve quality of life. The CDC also recommends regular screening tests, especially for people who are the risk of developing genetic cancers, for early detection. Certain types of vaccinations can also help lower the risk of known cervical and liver cancers. The risk can be further brought down by making healthy lifestyle choices, like changes in a diet.